Gestational diabetes is a condition that can develop during pregnancy, characterized by high blood sugar levels that typically resolve after childbirth. As you navigate through your pregnancy, it’s essential to understand how this condition arises and what it means for you and your baby. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect how your body processes insulin, leading to elevated glucose levels.
This condition usually emerges in the second or third trimester, and while it can be alarming, it is manageable with the right approach. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gestational diabetes is crucial. You may not experience any noticeable symptoms, which is why routine screening is vital.
Typically, healthcare providers will conduct a glucose tolerance test between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. If diagnosed, you will need to monitor your blood sugar levels closely and work with your healthcare team to develop a management plan tailored to your needs. Understanding the nature of gestational diabetes empowers you to take proactive steps in ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
Risks and Complications for Mother and Baby
Gestational diabetes can pose several risks for both you and your baby if not managed properly. For you, the condition increases the likelihood of developing high blood pressure and preeclampsia, which can lead to serious complications during pregnancy. Additionally, women with gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
This makes it essential for you to monitor your health closely and maintain regular check-ups even after your baby is born. For your baby, gestational diabetes can lead to excessive growth, known as macrosomia, which may complicate delivery and increase the risk of cesarean section. Furthermore, babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may experience low blood sugar levels shortly after birth, requiring immediate medical attention.
There is also a risk of respiratory distress syndrome and an increased likelihood of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. Understanding these risks can help you take the necessary precautions to safeguard both your health and that of your child.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels during Pregnancy

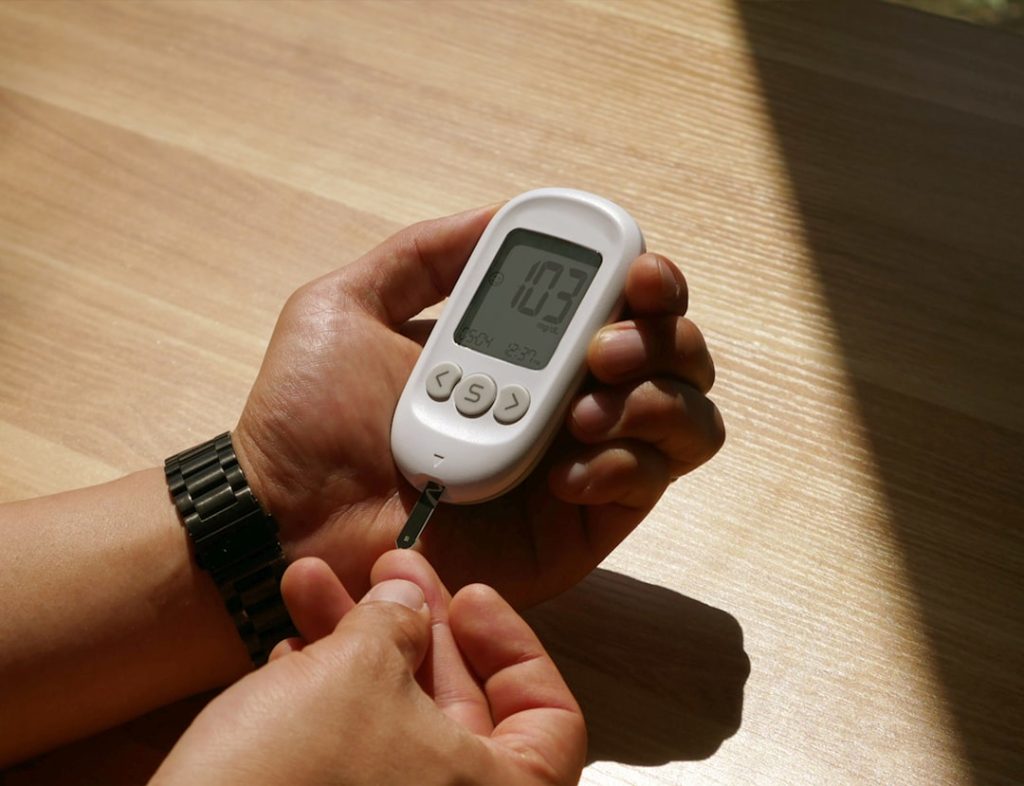
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of managing gestational diabetes effectively. You will likely be advised to check your blood sugar several times a day, typically before meals and occasionally after eating. This routine helps you understand how different foods affect your glucose levels and allows you to make informed dietary choices.
Keeping a log of your readings can also provide valuable insights for your healthcare provider, enabling them to adjust your management plan as needed. In addition to self-monitoring, regular appointments with your healthcare team are essential. They will assess your blood sugar trends and may recommend adjustments to your diet or exercise regimen based on your readings.
It’s important to communicate openly about any challenges you face in managing your blood sugar levels. By working collaboratively with your healthcare team, you can develop strategies that fit your lifestyle while ensuring the health of both you and your baby.
Healthy Eating and Exercise for Managing Diabetes during Pregnancy
Adopting a healthy eating plan is fundamental in managing gestational diabetes effectively. You should focus on consuming balanced meals that include a variety of nutrients while keeping an eye on carbohydrate intake. Incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables into your diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
It’s also beneficial to eat smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day rather than three large ones, as this can prevent spikes in glucose levels. Exercise plays a vital role in managing gestational diabetes as well. Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
You might consider activities such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga, which are generally safe during pregnancy. However, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it aligns with your specific health needs. Finding enjoyable ways to stay active can make it easier for you to incorporate exercise into your daily routine.
Medication and Insulin Management for Pregnant Women with Diabetes
In some cases, dietary changes and exercise alone may not be sufficient to manage gestational diabetes effectively. If your blood sugar levels remain elevated despite these efforts, your healthcare provider may recommend medication or insulin therapy. Insulin is often the preferred treatment during pregnancy because it does not cross the placenta and poses minimal risk to the baby.
Your healthcare team will guide you on how to administer insulin if needed and monitor its effects on both you and your baby. It’s important to remember that medication does not replace the need for a healthy lifestyle; rather, it complements it. You should continue to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and maintain open communication with your healthcare provider about any concerns or side effects you may experience from medication.
By taking a comprehensive approach that includes medication management alongside lifestyle changes, you can effectively control gestational diabetes and promote a healthy pregnancy.
Potential Long-Term Effects on the Baby

The implications of gestational diabetes extend beyond pregnancy itself; they can have long-term effects on your child’s health as well. Research indicates that children born to mothers with gestational diabetes may have an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life. This connection underscores the importance of maintaining healthy habits not only during pregnancy but also after childbirth.
By fostering a healthy environment for your child from an early age, you can help mitigate these risks. Additionally, there may be developmental considerations linked to gestational diabetes. Some studies suggest that children born to mothers with this condition may face challenges related to cognitive development or behavioral issues as they grow older.
While these outcomes are not guaranteed, they highlight the importance of ongoing health monitoring for both you and your child after delivery. Engaging in regular pediatric check-ups and promoting a balanced lifestyle can contribute positively to your child’s long-term health.
Preparing for Labor and Delivery with Diabetes
As you approach labor and delivery, preparing for the process with gestational diabetes in mind is essential. You should discuss your birth plan with your healthcare provider well in advance, ensuring that they are aware of your condition and any specific needs you may have during labor. It’s crucial to have a clear understanding of how your blood sugar levels will be monitored during this time, as stress and physical exertion can impact glucose levels.
In some cases, women with gestational diabetes may require additional interventions during labor, such as intravenous fluids or insulin administration if their blood sugar levels fluctuate significantly. Being informed about these possibilities can help alleviate anxiety as you prepare for delivery. Additionally, consider discussing postpartum care plans with your healthcare team so that you have a clear understanding of what to expect immediately after giving birth.
Postpartum Care and Managing Diabetes after Pregnancy
After delivering your baby, postpartum care becomes a priority, especially for managing diabetes effectively. It’s essential to have follow-up appointments scheduled with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood sugar levels after childbirth. Many women find that their blood sugar levels return to normal shortly after delivery; however, some may continue to experience elevated levels or develop type 2 diabetes later on.
You should also focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle post-pregnancy by continuing the dietary habits and exercise routines established during pregnancy. This proactive approach not only benefits your health but also sets a positive example for your child as they grow up. Engaging in regular check-ups will help ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly, allowing you to enjoy motherhood while prioritizing your well-being.
In conclusion, understanding gestational diabetes is crucial for managing this condition effectively throughout pregnancy and beyond. By staying informed about risks, monitoring blood sugar levels diligently, adopting healthy eating habits, considering medication when necessary, and preparing for labor and postpartum care, you can navigate this journey with confidence. Your proactive approach will not only benefit you but also contribute positively to the health of your baby now and in the future.