When you delve into the world of diabetes, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where your immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in your pancreas. This results in little to no insulin production, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels.
You may find that individuals diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes often experience symptoms in childhood or adolescence, although it can occur at any age. The management of this condition typically requires lifelong insulin therapy, as your body cannot produce the hormone on its own. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes is primarily characterized by insulin resistance, where your body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin.
Over time, your pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. This form of diabetes is more prevalent in adults, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adolescents due to rising obesity rates. Lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and weight management play a significant role in the development and management of Type 2 diabetes.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for recognizing how each type affects individuals differently and the specific approaches required for effective management.
Debunking Common Myths About Type 1 Diabetes
There are numerous myths surrounding Type 1 diabetes that can lead to misunderstandings about the condition. One prevalent myth is that Type 1 diabetes is caused by eating too much sugar or being overweight. This misconception can be particularly damaging, as it places blame on individuals for a condition that is largely beyond their control.
In reality, Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder with no known prevention methods. It’s important for you to understand that lifestyle choices do not cause this type of diabetes; rather, it results from genetic and environmental factors that trigger the immune response. Another common myth is that people with Type 1 diabetes cannot lead normal lives or participate in physical activities.
This belief can be disheartening for those living with the condition, as it suggests limitations that simply aren’t true. With proper management, including regular blood sugar monitoring and insulin administration, you can engage in sports, travel, and enjoy a variety of foods. Many individuals with Type 1 diabetes lead fulfilling lives, pursuing careers, hobbies, and relationships just like anyone else.
By debunking these myths, you can foster a more accurate understanding of Type 1 diabetes and support those affected by it.
Dispelling Misconceptions About Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is often surrounded by misconceptions that can perpetuate stigma and misunderstanding. One of the most common myths is that only overweight individuals develop this type of diabetes. While being overweight is a significant risk factor, it’s crucial to recognize that people of all body types can develop Type 2 diabetes.
Genetics, age, and lifestyle factors all contribute to your risk, and focusing solely on weight can overlook the complexity of this condition. Understanding that Type 2 diabetes can affect anyone helps to create a more inclusive dialogue about prevention and management. Another misconception is that Type 2 diabetes is a mild form of diabetes that doesn’t require serious attention.
This belief can lead to complacency in managing the condition, which can have severe long-term consequences. In reality, uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes can result in serious health complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss. It’s essential for you to recognize that managing Type 2 diabetes requires commitment and proactive measures, including regular check-ups, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications.
By dispelling these misconceptions, you can empower yourself and others to take charge of their health.
Identifying the Risk Factors for Type 1 Diabetes
Identifying the risk factors for Type 1 diabetes can be challenging since the exact cause remains unclear. However, certain genetic predispositions have been identified that may increase your likelihood of developing this autoimmune condition. If you have a family history of Type 1 diabetes or other autoimmune diseases, your risk may be higher.
While genetics play a role, environmental factors such as viral infections have also been suggested as potential triggers for the onset of Type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed individuals. Another important aspect to consider is that Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age, although it is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults. This unpredictability makes it crucial for you to be aware of the symptoms associated with the condition, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, and unexplained weight loss.
Early detection and intervention are vital for managing Type 1 diabetes effectively. By understanding these risk factors, you can be more vigilant about monitoring your health and seeking medical advice if necessary.
Recognizing the Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
When it comes to Type 2 diabetes, recognizing the risk factors is essential for prevention and early intervention. One of the most significant risk factors is being overweight or obese, particularly if excess weight is carried around the abdomen. This type of fat distribution is linked to insulin resistance, making it crucial for you to maintain a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle can further increase your risk; incorporating movement into your daily routine can significantly impact your overall health. Age is another critical factor in developing Type 2 diabetes; as you get older, your risk increases. This is particularly true after age 45 when metabolic changes may occur.
Furthermore, if you have a family history of diabetes or belong to certain ethnic groups—such as African American, Hispanic/Latino, Native American, or Asian American—you may be at a higher risk as well. Recognizing these risk factors empowers you to take proactive steps toward prevention through lifestyle changes and regular health screenings.
The Truth About Managing Type 1 Diabetes
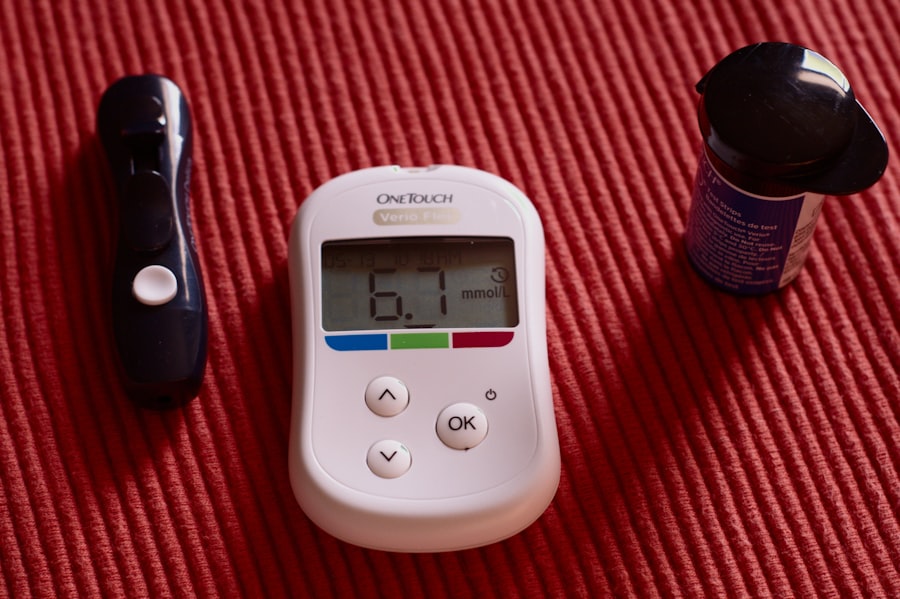

Managing Type 1 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes monitoring blood sugar levels, administering insulin, and making informed dietary choices. You must regularly check your blood glucose levels to ensure they remain within target ranges; this helps prevent both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Insulin therapy is a cornerstone of management; whether through injections or an insulin pump, finding the right dosage and timing is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Diet also plays a significant role in managing Type 1 diabetes. You need to be mindful of carbohydrate intake and how different foods affect your blood sugar levels. Learning to count carbohydrates and understanding how various foods impact your body will empower you to make healthier choices.
Additionally, regular physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity and improve overall well-being. By adopting a holistic approach to managing Type 1 diabetes, you can lead a fulfilling life while effectively controlling your condition.
The Reality of Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 diabetes involves a multifaceted approach that emphasizes lifestyle changes alongside medical interventions. You may need to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to understand how your body responds to different foods and activities. Depending on your individual circumstances, medication may also be necessary to help regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan that suits your needs. Dietary modifications are particularly important in managing Type 2 diabetes. You should focus on consuming whole foods rich in nutrients while minimizing processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats.
Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can also significantly improve insulin sensitivity and aid in weight management. Remember that managing Type 2 diabetes is an ongoing process; staying informed about your condition and making adjustments as needed will empower you to take control of your health.
Promoting Awareness and Education About Diabetes
Promoting awareness and education about diabetes is vital for fostering understanding and support within communities. You can play an active role by sharing information about both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes with friends, family, and colleagues. By dispelling myths and misconceptions surrounding these conditions, you contribute to a more informed society that recognizes the challenges faced by those living with diabetes.
Engaging in community events or online forums dedicated to diabetes education can also help raise awareness. These platforms provide opportunities for individuals affected by diabetes to share their experiences and learn from one another. Additionally, advocating for better access to healthcare resources and support services can make a significant difference in the lives of those managing diabetes.
By promoting awareness and education about this chronic condition, you help create a more supportive environment for everyone affected by diabetes.
