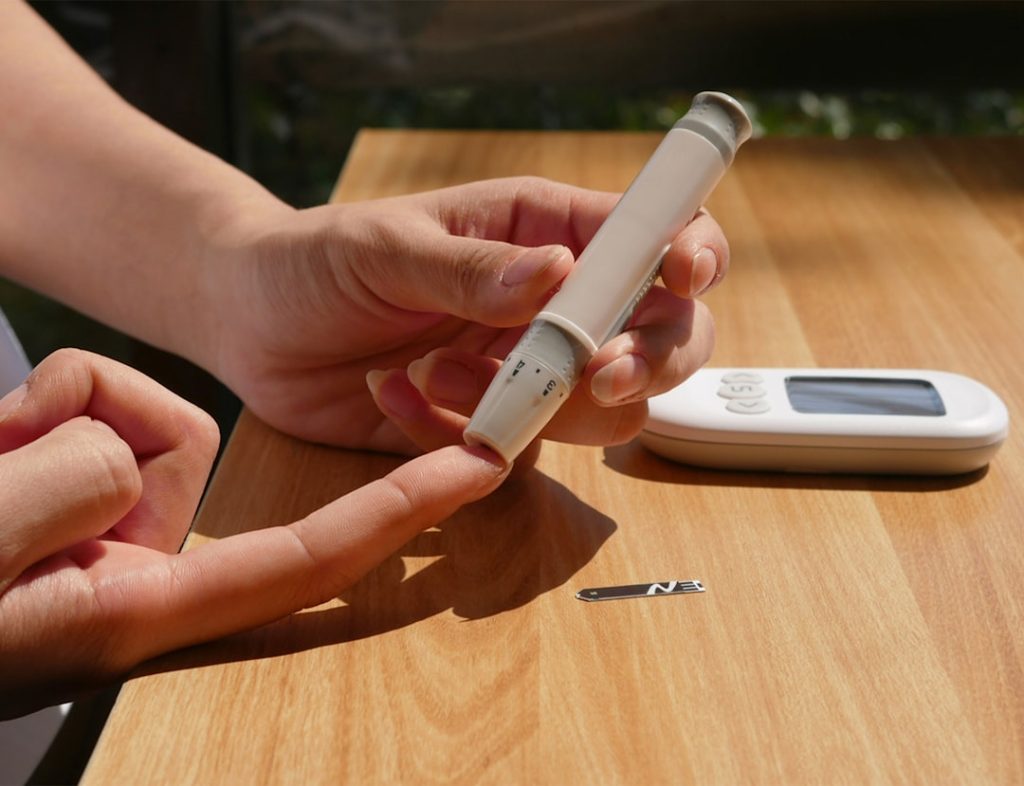
When it comes to managing diabetes, understanding the importance of testing blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. Regular monitoring allows you to gain insight into how your body responds to various foods, activities, and medications. By keeping a close eye on your blood sugar levels, you can make informed decisions that help maintain your health and prevent complications.
This proactive approach is essential for anyone living with diabetes, as it empowers you to take control of your condition and make adjustments as needed. Moreover, testing your blood sugar provides valuable data that can be shared with your healthcare team. This information helps them tailor your treatment plan to better suit your individual needs.
Whether you are adjusting your insulin dosage or modifying your diet, having accurate blood sugar readings is crucial for effective management. In essence, regular testing serves as a vital tool in your diabetes management arsenal, enabling you to live a healthier and more balanced life.
Key Takeaways
- Regular blood sugar testing is crucial for effective diabetes management and preventing complications.
- Testing frequency depends on factors like diabetes type, treatment plan, and individual health conditions.
- Type 1 diabetes typically requires more frequent testing compared to type 2 and gestational diabetes.
- Guidelines recommend adjusting testing frequency during illness, medication changes, or lifestyle shifts.
- Finding a personalized balance in testing helps optimize blood sugar control and overall health outcomes.
Factors Affecting How Often to Test Blood Sugar
Several factors influence how often you should test your blood sugar levels. One of the primary considerations is the type of diabetes you have. For instance, individuals with Type 1 diabetes often require more frequent testing compared to those with Type 2 diabetes.
This is largely due to the nature of insulin dependence and the need for constant monitoring to avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Understanding your specific type of diabetes is essential in determining an appropriate testing schedule. Another significant factor is your treatment regimen.
If you are on insulin therapy, you may need to test more frequently to ensure that your blood sugar levels remain stable throughout the day. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress can also impact how often you should check your levels. For example, if you are starting a new exercise program or making significant dietary changes, it may be wise to increase the frequency of your testing during this transition period.
By considering these various factors, you can create a personalized testing schedule that aligns with your unique circumstances.
Guidelines for Testing Blood Sugar

Establishing guidelines for testing blood sugar can help streamline the process and ensure that you are monitoring your levels effectively. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes test their blood sugar at various times throughout the day, including before meals and at bedtime. This approach allows you to capture a comprehensive picture of how your blood sugar fluctuates in response to different activities and food intake.
In addition to regular testing, it is also important to keep a log of your results. Documenting your blood sugar readings can help identify patterns and trends over time, making it easier to discuss with your healthcare provider. Furthermore, consider using technology such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) if they are available to you.
These devices provide real-time data and can alert you to significant changes in your blood sugar levels, offering an additional layer of support in managing your diabetes.
Frequency of Testing for Type 1 Diabetes
For those living with Type 1 diabetes, frequent blood sugar testing is often necessary due to the unpredictable nature of the condition. It is generally recommended that you test your blood sugar at least four to six times a day. This typically includes checking before meals, after meals, and before bedtime.
However, depending on your individual circumstances, you may need to test even more frequently, especially during periods of illness or when experiencing significant changes in routine. The rationale behind this frequency is rooted in the need for precise insulin management. Since Type 1 diabetes requires insulin administration based on blood sugar levels, having accurate readings allows you to adjust your doses accordingly.
Additionally, frequent testing helps you recognize patterns in your blood sugar fluctuations, enabling you to make informed decisions about food choices and physical activity. Ultimately, the goal is to maintain stable blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Frequency of Testing for Type 2 Diabetes
| Type of Diabetes | Testing Frequency | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | 4-10 times per day | Monitor blood sugar before and after meals, before and after exercise, at bedtime, and when feeling unwell | Frequent testing helps adjust insulin doses and prevent hypoglycemia |
| Type 2 Diabetes (on insulin) | Multiple times daily | Check blood sugar before meals and at bedtime | Frequency depends on insulin regimen and doctor’s advice |
| Type 2 Diabetes (not on insulin) | 1-2 times per day or less | Monitor blood sugar to assess control and medication effectiveness | May test less frequently if blood sugar is stable |
| Gestational Diabetes | 4 times per day | Test fasting and 1-2 hours after meals | Helps manage blood sugar for maternal and fetal health |
| Prediabetes | Occasional testing | Monitor blood sugar to track progression | Testing frequency varies; often done during routine checkups |
When it comes to Type 2 diabetes, the frequency of blood sugar testing can vary significantly based on individual treatment plans and lifestyle factors. If you are managing your condition through diet and exercise alone, you may not need to test as frequently as someone on insulin therapy. In many cases, testing once or twice a day may suffice, particularly if you are stable and not experiencing significant fluctuations in your blood sugar levels.
However, if you are taking oral medications or insulin for Type 2 diabetes, more frequent testing may be necessary. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best testing schedule for your specific situation. They can help assess how often you should check your blood sugar based on factors such as medication type, lifestyle changes, and overall health goals.
By finding the right balance in testing frequency, you can effectively manage your Type 2 diabetes and maintain optimal health.
Frequency of Testing for Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes presents its own unique challenges when it comes to blood sugar monitoring. If you have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes, it is crucial to test your blood sugar levels regularly to ensure both your health and the health of your baby. Typically, healthcare providers recommend that you test your blood sugar four times a day: upon waking and after each meal.
This schedule allows for comprehensive monitoring of how food intake affects your blood sugar levels throughout the day. The reason for this frequency is twofold: first, it helps ensure that your blood sugar remains within target ranges; second, it provides valuable information that can guide dietary choices and insulin management if needed. As pregnancy progresses, hormonal changes can affect insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, making regular testing even more critical.
By adhering to a consistent testing schedule during pregnancy, you can help mitigate risks associated with gestational diabetes and promote a healthier outcome for both you and your baby.
Adjusting Testing Frequency for Different Situations
Life is full of changes and unexpected events that can impact how often you need to test your blood sugar levels. For instance, if you are experiencing illness or stress, it may be necessary to increase the frequency of testing. Illness can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels due to changes in appetite or increased insulin resistance, while stress can lead to elevated glucose levels as well.
In these situations, being proactive about monitoring can help prevent complications and allow for timely adjustments in treatment. Additionally, if you are making significant lifestyle changes—such as starting a new exercise program or altering your diet—you may want to test more frequently during this transition period. This will help you understand how these changes affect your blood sugar levels and allow for necessary adjustments in medication or food intake.
Ultimately, being flexible with your testing schedule based on situational factors will empower you to manage your diabetes more effectively.
Finding the Right Balance for Blood Sugar Testing
In conclusion, finding the right balance for blood sugar testing is essential for effective diabetes management. The frequency at which you test will depend on various factors including the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, lifestyle changes, and any situational challenges that arise. By understanding these elements and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can develop a personalized testing schedule that meets your unique needs.
Regular monitoring not only helps maintain stable blood sugar levels but also empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. Whether you’re living with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes or managing gestational diabetes, staying attuned to your body’s signals through consistent testing will ultimately lead to better health outcomes. Remember that managing diabetes is a journey; by finding the right balance in testing frequency, you’re taking an important step toward achieving long-term wellness and quality of life.
