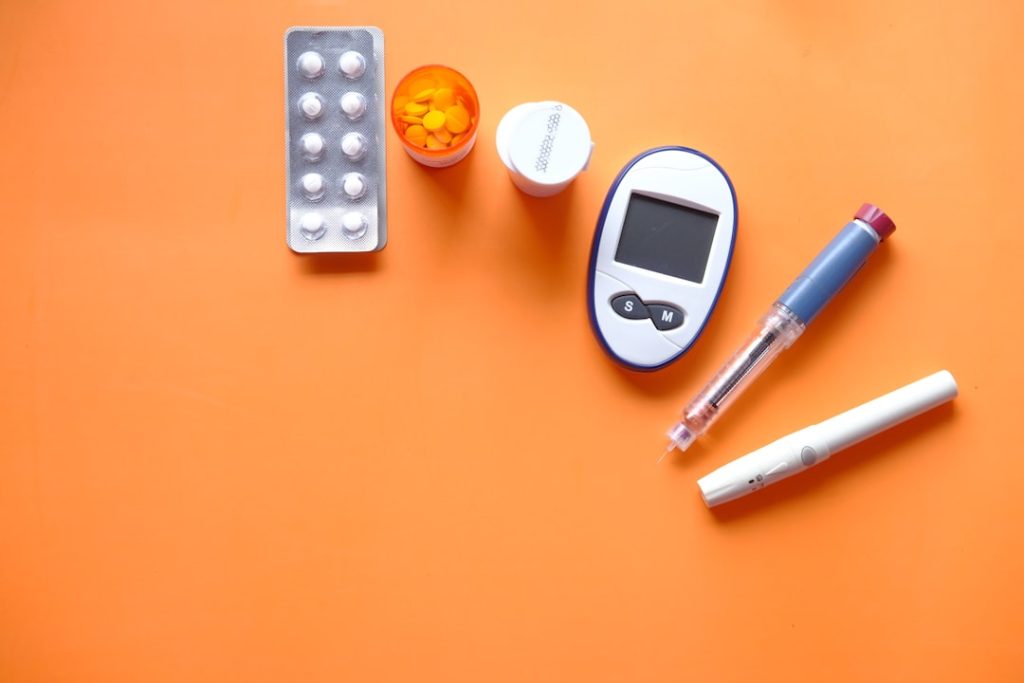
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your child’s body processes glucose, a vital source of energy. There are primarily two types of diabetes that can occur in children: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
This type often manifests in childhood or adolescence, and it requires lifelong management. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes, which is increasingly being diagnosed in younger populations, is often linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for you as a parent or caregiver, as it shapes the approach to treatment and management.
The prevalence of diabetes among children has been rising alarmingly, making it essential for you to be informed about the condition. According to recent statistics, millions of children worldwide are living with diabetes, and this number continues to grow. The implications of diabetes extend beyond physical health; they can also affect your child’s emotional well-being and social interactions.
By understanding diabetes, you can better support your child in navigating the challenges that come with this condition, ensuring they lead a fulfilling life despite their diagnosis.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes in Children
As a parent or caregiver, being vigilant about the signs and symptoms of diabetes in children is vital for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. If you notice that your child is drinking more fluids than usual or waking up multiple times at night to use the bathroom, these could be red flags indicating a potential issue with blood sugar regulation.
Additionally, children with diabetes may experience irritability or mood swings due to fluctuating blood sugar levels, which can be distressing for both you and your child. Other symptoms may include blurred vision and slow-healing wounds. If your child seems to be experiencing these symptoms consistently, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Early recognition can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, which is crucial in managing diabetes effectively. By being aware of these signs, you empower yourself to take proactive steps in safeguarding your child’s health.
Diagnosing Diabetes in Children
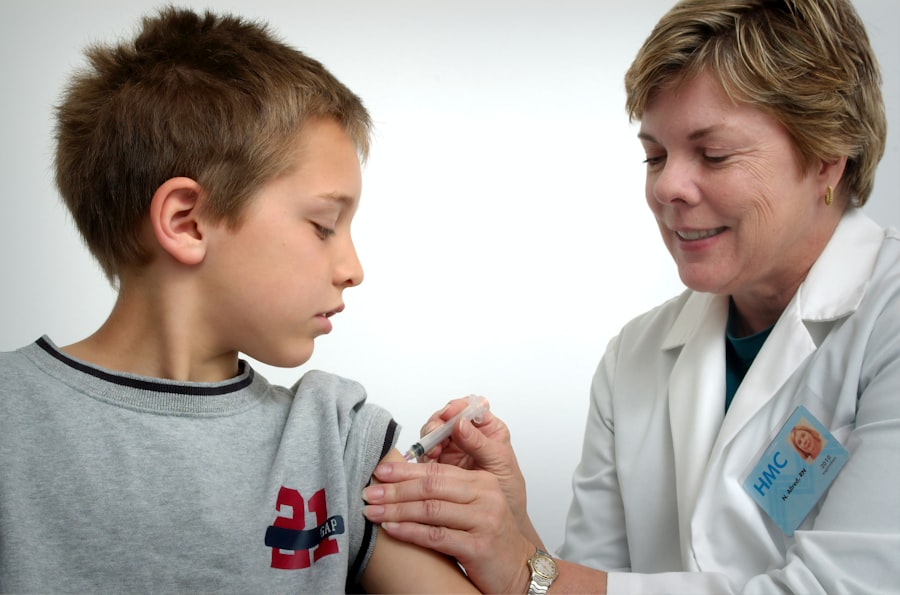
When it comes to diagnosing diabetes in children, healthcare professionals typically rely on a combination of medical history, physical examinations, and specific blood tests. If you suspect that your child may have diabetes based on observed symptoms, the first step is to schedule an appointment with a pediatrician. They will likely conduct a fasting blood glucose test or an A1C test to measure your child’s average blood sugar levels over the past few months.
An A1C level of 6.5% or higher is generally indicative of diabetes. In some cases, your healthcare provider may also perform an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which involves measuring blood sugar levels after fasting and then again two hours after consuming a sugary drink. This comprehensive approach ensures that any diagnosis made is accurate and reliable.
Understanding the diagnostic process can help alleviate some of your concerns and prepare you for what lies ahead in terms of treatment and management.
Managing Diabetes in Children: Treatment Options
Once a diagnosis of diabetes is confirmed, managing the condition becomes a priority for you and your child. Treatment options vary depending on whether your child has Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. For Type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential since the body no longer produces insulin.
You will need to work closely with healthcare providers to determine the appropriate type and dosage of insulin for your child. This may involve multiple daily injections or the use of an insulin pump, which can provide more consistent blood sugar control. For Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in management.
Your healthcare team may recommend a combination of oral medications, dietary changes, and increased physical activity. It’s crucial for you to be involved in this process, as your support can significantly impact your child’s adherence to treatment plans. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers will help monitor your child’s progress and make necessary adjustments to their treatment regimen.
The Role of Diet and Exercise in Managing Diabetes in Children
Diet and exercise are cornerstones of effective diabetes management for children. As a parent or caregiver, you play a pivotal role in shaping your child’s eating habits and encouraging physical activity. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels.
It’s essential to work with a registered dietitian who specializes in pediatric diabetes to create meal plans that are not only nutritious but also enjoyable for your child. Incorporating regular physical activity into your child’s routine is equally important. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and can lower blood sugar levels.
Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity each day; this could include playing sports, riding bikes, or even dancing at home. By making physical activity a fun part of your family’s lifestyle, you can help your child develop healthy habits that will benefit them throughout their life.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels in Children with Diabetes
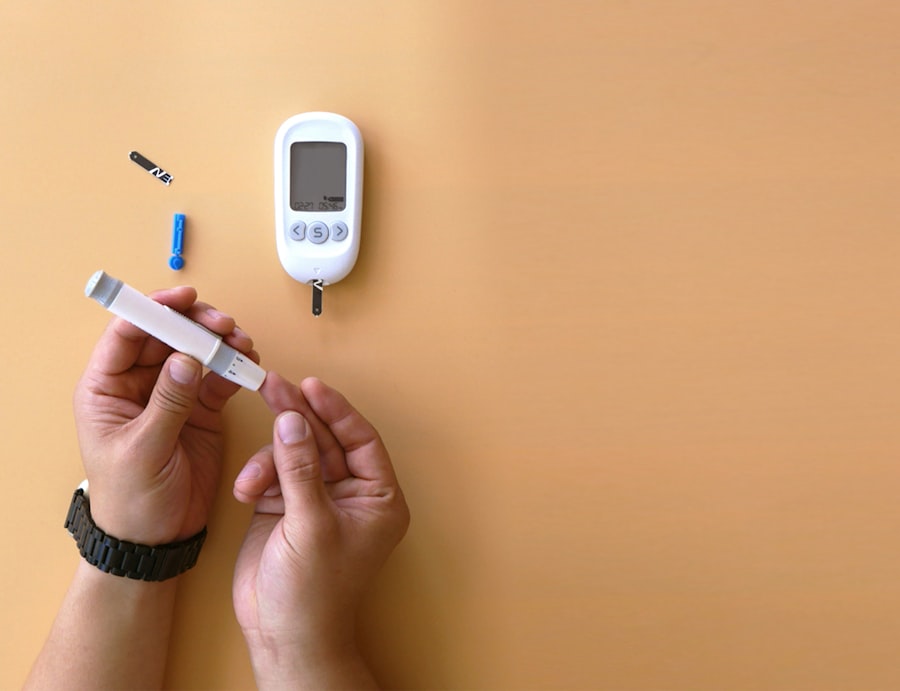
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of managing diabetes in children. As a parent or caregiver, you will need to learn how to check your child’s blood glucose levels regularly using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Keeping track of these levels helps you understand how different foods, activities, and stressors affect your child’s blood sugar.
It’s essential to establish a routine for monitoring—whether it’s before meals, after exercise, or at bedtime—to ensure that you have a comprehensive view of their glucose patterns. In addition to regular monitoring, maintaining a log of blood sugar readings can be beneficial for both you and your healthcare team. This log can help identify trends over time and inform necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
By actively participating in this monitoring process, you empower yourself to make informed decisions about your child’s care while also teaching them the importance of self-management as they grow older.
Preventing Complications of Diabetes in Children
Preventing complications associated with diabetes is crucial for ensuring your child’s long-term health and well-being. Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems over time. As a parent or caregiver, staying vigilant about maintaining target blood sugar levels through proper management is essential in reducing these risks.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are vital for monitoring potential complications early on. These visits may include eye exams, kidney function tests, and assessments of cardiovascular health. Educating yourself about the potential complications associated with diabetes will enable you to advocate for your child’s health effectively.
By fostering open communication with healthcare professionals and being proactive about preventive measures, you can help safeguard your child’s future.
Supporting Children with Diabetes: Tips for Parents and Caregivers
Supporting a child with diabetes requires patience, understanding, and active involvement in their care journey. One of the most important things you can do as a parent or caregiver is to foster an open dialogue about their condition. Encourage your child to express their feelings and concerns regarding their diabetes; this emotional support can significantly impact their mental well-being.
Additionally, consider involving your child in their own care as they grow older. Teaching them how to monitor their blood sugar levels, administer insulin if applicable, and make healthy food choices empowers them to take charge of their health. Creating a supportive environment at home where healthy habits are encouraged will not only benefit your child but also promote overall family wellness.
In conclusion, managing diabetes in children is a multifaceted process that requires education, vigilance, and support from parents and caregivers like you. By understanding the condition thoroughly and being proactive about treatment options, diet, exercise, monitoring blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and providing emotional support, you can help your child lead a healthy and fulfilling life despite their diagnosis.